How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient industrial inspections. This guide provides a structured approach to learning drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic maneuvers to advanced techniques and safety regulations. We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, understand flight controls, and delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial footage.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. We’ll break down complex concepts into manageable steps, providing clear explanations and helpful visuals to enhance your learning experience. By the end of this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to operate your drone with confidence and proficiency, ensuring both safe and successful flights.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the different parts of your drone and the terminology used is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key components and provides a glossary of common terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Each component plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. A basic understanding of their individual roles ensures you can troubleshoot problems and operate your drone more efficiently.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Motor performance is critical for flight stability and speed.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” processing data from various sensors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It coordinates motor speeds to control altitude, direction, and movement.
- Battery: The power source for the drone, providing energy to the motors and other electronic components. Battery life significantly impacts flight time.
- Camera: Captures images and videos. Camera quality varies greatly depending on the drone model, influencing image resolution, video quality, and features like image stabilization.
- Transmitter: The remote control used to pilot the drone, sending signals to the flight controller to control its movements.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms enhances your understanding of operation manuals and online resources.
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Altitude Hold | Maintains a consistent height above ground level. | The drone automatically adjusts its throttle to stay at 10 meters. |
| Gimbal | A stabilized mount for the camera, ensuring smooth footage even during flight maneuvers. | A three-axis gimbal minimizes camera shake during flight. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | An automated function that guides the drone back to its takeoff point. | Low battery triggers the RTH function, returning the drone safely. |
| Yaw | Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis. | Turning the drone left or right. |
Drone Battery Comparison
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics. Understanding these differences helps optimize flight time and performance.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S | 11.1 | 1300 | 15-20 |
| LiPo 4S | 14.8 | 1500 | 20-25 |
| LiHV 3S | 12.6 | 1500 | 18-22 |
| LiHV 4S | 16.8 | 1800 | 25-30 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and successful drone operation. This minimizes risks and ensures optimal performance.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This checklist should be followed before every flight to ensure the drone is in optimal condition.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or body.
- Check battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Check transmitter battery level and connection to the drone.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Confirm you are in a permitted flight area and are aware of airspace restrictions.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibration ensures accurate readings from the drone’s internal sensors, which are crucial for stable and controlled flight.
The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model, but generally involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern, allowing the sensors to adjust to their environment.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight steps can aid in a consistent and thorough inspection process.
The flowchart would visually depict the steps listed in the Pre-Flight Checklist above, using boxes and arrows to illustrate the sequence of actions. Each box would represent a specific check, and arrows would indicate the flow from one check to the next. The flowchart would conclude with a decision point: “Drone ready for flight? Yes/No”.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are paramount for avoiding accidents and protecting your drone. This section covers various techniques and best practices.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The process varies slightly depending on the drone model and environment, but generally involves a controlled ascent and descent.
- Open Field Takeoff: Find a clear, level area free of obstacles. Slowly increase throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady ascent.
- Confined Space Takeoff: Carefully assess the space available, ensuring ample clearance from obstacles. A gentle, controlled ascent is essential. Assisted takeoff features (if available) can be helpful.
- Landing: Slowly descend the drone vertically, maintaining control and avoiding sudden movements. Once close to the ground, gently reduce throttle until it touches down smoothly.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Different techniques cater to various situations and drone capabilities.
- Assisted Takeoff: A feature on many drones that simplifies the takeoff process, often using GPS and other sensors to ensure a stable and controlled ascent.
- Manual Takeoff: Requires more skill and control, giving the pilot greater precision but demanding more experience.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Being prepared for unexpected events is crucial for safe drone operation.
- Wind Gusts: Maintain control of the drone by adjusting the sticks to counteract the wind. If the wind is too strong, land immediately.
- Low Battery: Initiate the Return-to-Home (RTH) function immediately if the battery is critically low. Land the drone as soon as possible.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the functions of the transmitter controls is fundamental to piloting a drone. This section covers basic maneuvers and a step-by-step guide to flying a square pattern.
Transmitter Controls
The transmitter sticks and buttons control the drone’s movement in three dimensions.
- Throttle Stick: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Yaw Stick: Controls rotation around the vertical axis (left and right turns).
- Pitch Stick: Controls movement forward and backward.
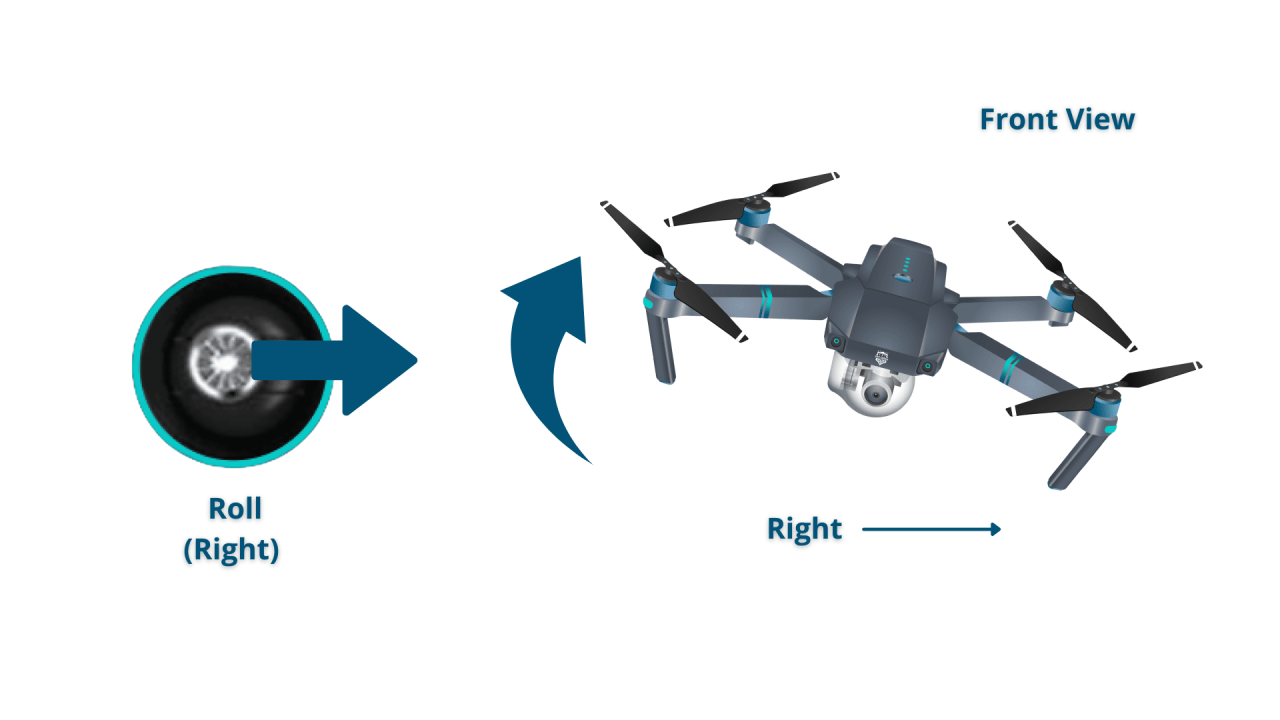
- Roll Stick: Controls movement left and right (sideways).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
These maneuvers form the foundation of drone piloting.
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Forward/Backward Flight: Moving the drone forward or backward.
- Turning: Rotating the drone left or right.
- Side-to-Side Movement: Moving the drone left or right.
Flying a Square Pattern
A step-by-step guide to practicing basic maneuvers.
- Take off and hover.
- Move forward a set distance.
- Turn 90 degrees to the right.
- Move forward the same distance.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 until a square is formed.
- Return to the starting point.
- Land the drone.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced techniques enhance drone capabilities and allow for more complex and creative flights. This section covers waypoint navigation, RTH adjustments, and troubleshooting common flight errors.
Waypoint Navigation and RTH
These features offer increased control and safety.
- Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated function that returns the drone to its takeoff point, useful in case of low battery or loss of signal.
Optimizing Drone Settings for Weather Conditions

Adjusting drone settings based on weather conditions ensures optimal performance and safety.
In windy conditions, reducing speed and increasing agility settings can help maintain control. In low-light conditions, adjusting camera settings like ISO and shutter speed becomes crucial for clear image capture.
Common Drone Flight Errors and Solutions
This list provides solutions to frequently encountered problems.
- Problem: Drone drifts during hover. Possible Cause: Uncalibrated sensors or wind. Solution: Calibrate sensors and adjust flight settings.
- Problem: GPS signal loss. Possible Cause: Obstructions or weak signal. Solution: Fly in open areas with a clear view of the sky.
- Problem: Motor failure. Possible Cause: Damaged motor or low battery. Solution: Inspect motors and replace if necessary; ensure adequate battery power.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings is crucial for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section covers various camera settings and steps for transferring footage.
Drone Camera Settings
These settings influence the quality and appearance of your drone footage.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is crucial before attempting complex flights, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to safe landing procedures. With practice and a solid understanding of the principles, you’ll soon be confidently operating your drone.
- Resolution: Determines the image size and detail (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light (higher ISO for low-light situations).
- Shutter Speed: The length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light (affects motion blur).
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera (affects depth of field).
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos, How to operate a drone

These tips enhance the quality of your aerial imagery.
- Use the highest resolution settings possible.
- Adjust ISO and shutter speed to match lighting conditions.
- Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives.
- Use image stabilization features to reduce camera shake.
Transferring Drone Footage
This process varies depending on the drone model but typically involves connecting the drone to a computer using a USB cable or SD card reader.
Most drone software will allow for the easy transfer of files to a computer once the drone is connected. Once transferred, the footage can then be edited using video editing software.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and the capabilities of your specific drone model. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your flying skills.
Safe and responsible drone operation is crucial for both personal safety and the protection of others.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to regulations and best practices is crucial for responsible drone operation. This section covers legal requirements, safety tips, and risk mitigation.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations before flying. These often involve registering your drone, obtaining necessary permits, and respecting airspace restrictions near airports or other sensitive areas.
Responsible Drone Operation
These tips contribute to safe and responsible flying.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near people or crowds.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Be mindful of privacy concerns and avoid filming people without their consent.
Potential Risks and Mitigation
Understanding potential risks allows for effective mitigation strategies.
- Risk: Drone malfunction. Mitigation: Regular maintenance and pre-flight checks.
- Risk: Loss of control. Mitigation: Proper training and adherence to safety guidelines.
- Risk: Collision with obstacles. Mitigation: Careful flight planning and obstacle avoidance.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section provides solutions for common drone problems and guides for basic maintenance and repairs.
Troubleshooting Guide
This table Artikels solutions to frequent problems.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge or high power consumption | Charge battery fully; optimize flight settings for lower power consumption |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, weak signal, or GPS module malfunction | Fly in open areas; check GPS module; recalibrate GPS |
| Motor Failure | Damaged motor or loose connections | Inspect motor for damage; check and tighten connections |
| Drone Won’t Turn On | Low battery, faulty power switch, or other electronic failure | Charge the battery, check the power switch, and inspect the drone for other potential problems. |
Basic Drone Maintenance and Repairs
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone.
This would include cleaning propellers, checking motor mounts for tightness, inspecting battery connections, and ensuring the overall integrity of the drone’s body. Minor repairs, such as replacing damaged propellers, might be undertaken depending on the user’s skill and comfort level.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Understanding composition principles enhances the visual appeal of your aerial footage. This section covers shot types and camera angles.
Principles of Composition
Applying basic photographic composition rules enhances the impact of your aerial imagery.
This includes the rule of thirds, leading lines, and creating visual balance within the frame. The use of negative space and strategic placement of subjects within the frame can also significantly improve the visual appeal of the final image.
Different Shot Types
These shot types provide various perspectives and storytelling opportunities.
- Aerial Shots: Wide shots showcasing a landscape or scene from above.
- Tracking Shots: Following a subject as it moves across the scene.
- Establishing Shots: Wide shots that set the scene and establish the location.
Camera Angles and Their Effects
Different angles create varying moods and perspectives.
A high angle shot, looking down on the subject, can create a sense of dominance or smallness. A low angle shot, looking up at the subject, can convey power or grandeur. A bird’s-eye view shot provides a comprehensive overview of the scene, while a Dutch angle can introduce a sense of unease or chaos. The use of different camera angles allows for greater creative control and flexibility.
Operating a drone successfully involves a combination of careful preparation, precise control, and a deep understanding of safety protocols. From pre-flight checklists to advanced flight maneuvers, this guide has provided a framework for responsible and efficient drone operation. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to regulations are crucial for honing your skills and ensuring safe flight operations. Embrace the learning process, explore the possibilities, and capture the world from a unique perspective with your drone.
Question Bank: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and ease-of-use features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have a “Return to Home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, carefully maneuver the drone back to your location using visual references.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced interference.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local government’s aviation authority website or a reputable drone resource for specific regulations in your area.
